Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Volt as Unit of Potential Difference, Resistivity of Various Materials, Conductance & Unit of Electrical Resistivity etc.
Important Questions on Ohm's Law
A wire of resistance is gradually stretched to double its original length. It is then cut into two equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel across a battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
A physical quantity, associated with electrical conductivity, has the SI unit ohm-meter. Identify this physical quantity.
A voltage of is applied across a carbon resistor with first, second and third rings of blue, black and yellow colours respectively. Calculate the value of current, in , through the resistor.
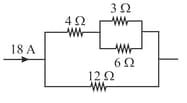
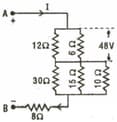
In the electrical network shown in the figure, the potential difference across resistance will be
State Ohm's law. Draw a graph between voltage and current for a metallic conductor.
To verify Ohm's law, a student is provided with a test resistor, a high resistance , a small resistance , two identical galvanometers and , and a variable voltage source . The correct circuit to carry out the experiment is
Determine the conductance (in Mho) of a conductor, when the value of current that flows through the conductor is 2 A and the potential difference between the ends of the conductor is 40 V.
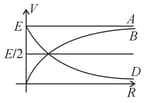
A cell of emf having an internal resistance is connected to an external resistance . The potential difference across the resistance varies with as shown by the curve,
Two rods of copper and iron with the same cross sectional area are joined at and a steady current flows through the rods as shown in the figure.
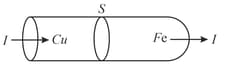
Choose the most appropriate representation of charges accumulated near the junction .
In the figure the potential difference across resistor is . Then the potential difference between and is
Two metal slabs of equal lengths, equal cross sectional areas and having resistances in the ratio are connected first in series and then in parallel separately. The ratio of their effective conductivities is
A graph drawn between current and voltage in a conductor is as shown in the figure. The changes in the resistance in and parts respectively
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased by . Due to the consequent decrease in diameter the change in the resistance of the wire will be
The specific resistance of a wire is its volume is and its resistance is ohms, then its length will be:-
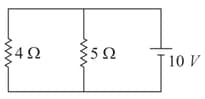
In the following diagram current in the resistor is (when the internal resistance of the battery is zero) :-